by Vlad Ungureanu
Jun 2020
Key takeaways from this article!
Personality describes an individual's expression of different high order traits or characteristics.
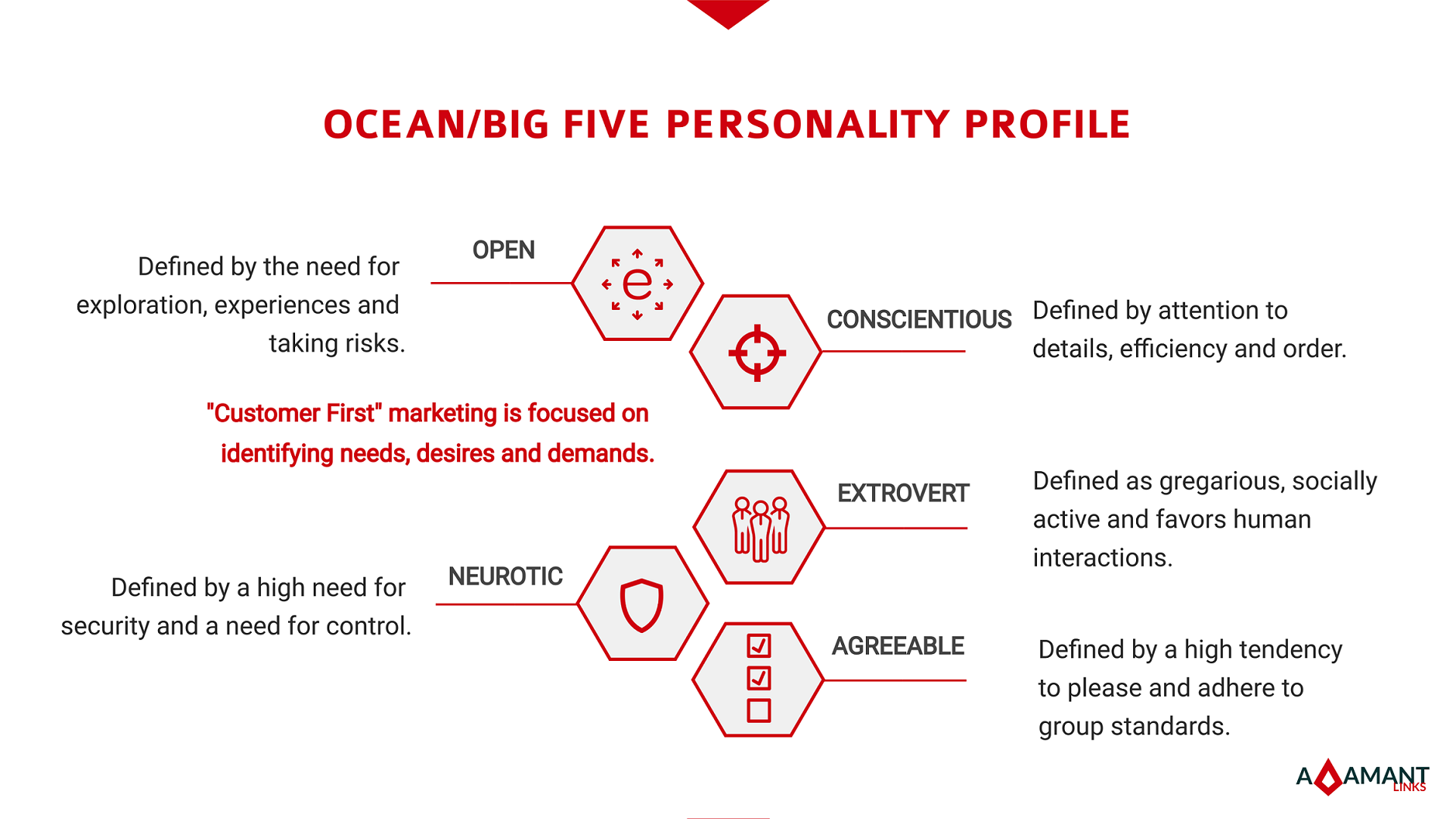
People open to experience tend to be more adventurous and creative, they are imaginative, curious and prefer novelty over routine.
Conscientious people are disciplined, resourceful, hard-working and achievement striving. They prefer stability, order and a high sense of control.
Extrovert people are energetic, friendly, gregarious and like to be in the centre of attention. They are optimistic and show high levels of self-confidence.
Agreeable people are warm, altruistic, helpful and humble. They believe in cooperation, moderation and conformity.
Neurotic people are anxious, moody, fearful and sensitive. They have a high need for security and are frequently impulsive.
What is the Big Five/OCEAN Personality Model?
The Big Five personality traits, also known as the five-factor model (FFM) and the OCEAN model, is a taxonomy, or grouping, for personality traits. The Big Five/OCEAN model is meant to describe an individual based on their expression of the following five dimensions (or high order traits): openness to experience, conscientiousness, extraversion, agreeableness and neuroticism.
Every individual manifests each of the five broad dimensions of the Big Five/OCEAN personality model to one degree or another. In normal circumstances psychologists use questionnaire-based testing to measure the degree to which each of the traits is individually manifested for a specific person. The five-factor model captures the higher-order traits that include almost any other trait described by other personality models, making it one of the most used personality models to date.
Adamant Links - Big Five/OCEAN Model
OPENNESS TO EXPERIENCE
This trait features dominant characteristics such as imagination, insight and novelty. People who are high in this trait also tend to have a broad range of interests, enjoy arts, music and poetry. They are curious about the world and other people, they are eager to learn new things and enjoy new experiences.
People who are high in this trait tend to be more adventurous and creative; they also experience deeper and more differentiated emotional states. People low in this trait are often much more traditional and may struggle with abstract thinking.
Defining Traits:
- Exploration
- New Things
- New Experiences
- Rich Imagination
- Creative
- Complexity
- Variety
- Insight
- Brave (with a low need for security)
- Enjoy Arts or Artistic Activities
- Creative Hobbies
- Learner
- Peaceful
- Universal Values
- Moderate Impulsivity
In terms of marketing, openness to experience characterizes individuals who are willing to consider different points of view and opinions. As such, they are more likely to try to find the newest and most valuable offers, not being satisfied with routine. People high in openness to experience are also more likely to engage in online searches, browsing behavior and online purchases. The openness to experience dimension is positively correlated with both utilitarian and hedonistic motivation for shopping.
CONSCIENTIOUSNESS
The features of this dimension include high levels of thoughtfulness, good impulse control, and goal-directed behaviours. Highly conscientious people tend to be organized and mindful of details. They plan ahead, think about how their behaviour affects others, and are mindful of deadlines.
Defining Traits:
- Consistent
- Persistent
- Predictable
- Control (with a high need for security)
- Reliability
- Planning
- Resourceful
- Hard Working
- Efficient
- Organisation
- Perfectionism
- Ordered
- Discipline
In terms of marketing, conscientiousness does not have a significant positive effect on online buying, a possible explanation being the need to avoid the perceived risks of online purchases. Shopping motivation is highly utilitarian and their activity on social media is limited.
EXTROVERSION
Extroversion (or extraversion) is characterized by excitability, sociability, talkativeness, assertiveness, and high amounts of emotional expressiveness. People who are high in extroversion are outgoing and tend to gain energy in social situations. Being around other people helps them feel energized and excited.
People who are low in extroversion (or introverted) tend to be more reserved and have less energy to manifest in social settings. Social events can feel draining and introverts often require a period of solitude and quiet in order to "recharge".
Defining Traits:
- Sociable
- Assertive
- Outgoing
- Talkative
- Fun Loving
- Social Confidence
- Friendliness
- Non-conformist
- Pleasure Seeking
- Overconfident (with a very low need for security)
- Optimistic
- Energetic
In terms of marketing, extrovert people have a dominant behaviour of being in search of sensations. Extroversion makes individuals more receptive to change, to new things and ideas and makes them want social recognition, power and a certain status. Extroverts seek a high level of socialization, share their experiences with others and in the buying process they are willing to follow the suggestions of others. There is a positive relationship between extroversion and hedonistic motivation. Also, out of the Big Five dimensions, extroverts are the most active on social media and have a high use of smartphones.
AGREEABLENESS
This personality dimension includes attributes such as trust, altruism, kindness, affection, and other pro-social behaviours. People who are high in agreeableness tend to be more cooperative while those low in this trait tend to be more competitive and sometimes even manipulative.
Defining Traits:
- Altruist
- Trusting
- Humble
- Patience
- Helpful
- Sensitive
- Moderate
- Polite
- Tradition
- Conformity
- Cooperation
- Interest in Others
- Empathy
Although potential customers that have agreeableness as a predominant personality dimension are more easily influenced by the aesthetics of websites and find pleasure in interacting with other online shoppers, they process information and seek alternatives when buying online, counting more on the utilitarian value.
NEUROTICISM
Neuroticism is a trait characterized by sadness, moodiness, and emotional instability. Individuals who are high in this trait tend to experience mood swings, anxiety, irritability, and sadness. Those low in this trait tend to be more stable and emotionally resilient.
Defining Traits:
- Pessimism
- Moody
- Fear
- Anxiety
- Timid
- Insecure (very high need for security)
- Unstable
- Sensitive
- External Locus of Control
- Looks for Guidance
- External Decision Making
- Anger
- Frustration
- Lack of Self-Control
- High Impulsivity
- Agitated
Neuroticism is defined as the disruption in the emotional stability through negatively charged emotional states. People with neurotic personality are anxious, isolated and unsociable and avoid situations in which they must take control. There is a negative relationship between computer use and neuroticism. The more neurotic a person is, the harder it is to control emotions and refrain from buying a whim .
In the decision making process of a purchase, neurotics will evaluate whether the purchase that they are about to make will attract the attention of others. Moreover, they will try to reduce negative cognitive reactions for consumption by buying products at low prices and by comparing prices of different vendors. As such, the more neurotic the buyer’s personality is, the more prone the person will be to an utilitarian shopping motivation.
Neuroticism, openness and agreeableness have a small but significant influence on the willingness to shop online. There is a significant and positive relationship between openness to experience and online shopping frequency. Individuals in search of sensations and those who are authoritarian are more likely to make purchases online. The tendency to trust in the intentions and motivations of others has a significant influence on online purchase frequency.
References:
- "Personality influence on online stores customer behavior", Costinel Dobre and Anca-Maria Miclovan, 2015
- "Antecedents of computer self-efficacy: A study of the role of personality traits and gender", Huma Saleem, Anne Beaudry and Anne-Marie Croteau, 2011
- "Exploring the impact of personality traits on online shopping behavior", Wen-Chin Tsao and Hung-Ru Chang, 2010
- "Un posibil model de integrare a rezultatelor la inventarul NEO PI-R în cadrul demersului de evaluare specific selecţiei de personal" (Romanian language only), Viorel Robu, 2007
- "Personality determinants of online shopping: Explaining online purchase intentions using a hierarchical approach", Michael Bosnjaka, Mirta Galesic and Tracy Tuten, 2007
In our next article, get a detailed look at psychographic segmentation:
Psychographic Segmentation
-
Market Segmentation: Overview
FEB 2020 -
Market Segmentation: Demographics
MAR 2020 -
Market Segmentation: Geographic Location
MAR 2020 -
Big Five/OCEAN Personality Model
JUN 2020 -
Psychographic Segmentation
JUL 2020 -
Psychographics and Biological Gender
JUL 2020 -
Psychographics and Age
JUL 2020 -
Psychographics and Other Demographic Segments
JUL 2020 -
Psychographics and Individual Preferences
AUG 2020 -
Psychographics and Internal Values
AUG 2020 -
Psychographics and Shopping Motivation
AUG 2020 -
Psychographics and Social Media - Part I
AUG 2020 -
Psychographics and Social Media - Part II
SEP 2020 -
Psychographics and Persuasion - Part I
MAR 2021 -
Psychographics and Persuasion - Part II
APR 2021 -
Psychographics and Persuasion - Part III
APR 2021